Emitting Events in Native Modules
In some circustamces, you may want to have a Native Module that listen to some events in the platform layer and then emit them to the JavaScript layer, to let you application react to such native events. In other cases, you might have long running operations that can emits events so that the UI can be updated when those happen.
Both are good use cases for emitting events from a Native Modules. In this guide, you'll learn how to do that.
Emitting an Event when a new key added to the storage
In this example, you will learn how to emit an event when a new key is added to the storage. Changing the value of the key will not emit the event, but adding a new key will.
This guide starts from the Native Module guide. Make sure to be familiar with that guide before diving into this one, potentially implementing the example in the guide.
Step 1: Update the Specs of NativeLocalStorage
The first step would be to update the specs of the NativeLocalStorage specs to let React Native aware that the module can emit events.
- TypeScript
- Flow
Open the NativeLocalStorage.ts file and update it as it follows:
import type {TurboModule} from 'react-native';
import {TurboModuleRegistry} from 'react-native';
+import type {EventEmitter} from 'react-native/Libraries/Types/CodegenTypes';
+export type KeyValuePair = {
+ key: string,
+ value: string,
+}
export interface Spec extends TurboModule {
setItem(value: string, key: string): void;
getItem(key: string): string | null;
removeItem(key: string): void;
clear(): void;
+ readonly onKeyAdded: EventEmitter<KeyValuePair>;
}
export default TurboModuleRegistry.getEnforcing<Spec>(
'NativeLocalStorage',
);
Open the NativeLocalStorage.js file and update it as it follows:
// @flow
import type {TurboModule} from 'react-native';
import {TurboModule, TurboModuleRegistry} from 'react-native';
+import type {EventEmitter} from 'react-native/Libraries/Types/CodegenTypes';
+export type KeyValuePair = {
+ key: string,
+ value: string,
+}
export interface Spec extends TurboModule {
setItem(value: string, key: string): void;
getItem(key: string): ?string;
removeItem(key: string): void;
clear(): void;
+ onKeyAdded: EventEmitter<KeyValuePair>
}
export default (TurboModuleRegistry.get<Spec>(
'NativeLocalStorage'
): ?Spec);
With the import type statement, you are importing the EventEmitter type that is required to then add the onKeyAdded property.
When the event is emitted, you expect for it to receive a parameter of type string.
Step 2: Generate Codegen
Given that you have updated the specs for your Native Module, you now have to rerun Codegen to generate the artifacts in the native code.
This is the same process presented in the Native Modules guide.
- Android
- iOS
Codegen is executed through the generateCodegenArtifactsFromSchema Gradle task:
cd android
./gradlew generateCodegenArtifactsFromSchema
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 837ms
14 actionable tasks: 3 executed, 11 up-to-date
This is automatically run when you build your Android application.
Codegen is run as part of the script phases that's automatically added to the project generated by CocoaPods.
cd ios
bundle install
bundle exec pod install
The output will look like this:
...
Framework build type is static library
[Codegen] Adding script_phases to ReactCodegen.
[Codegen] Generating ./build/generated/ios/ReactCodegen.podspec.json
[Codegen] Analyzing /Users/me/src/TurboModuleExample/package.json
[Codegen] Searching for Codegen-enabled libraries in the app.
[Codegen] Found TurboModuleExample
[Codegen] Searching for Codegen-enabled libraries in the project dependencies.
[Codegen] Found react-native
...
Step 3: Update the App code
Now, it's time to update the code of the App to handle the new event.
Open the App.tsx file and modify it as it follows:
import React from 'react';
import {
+ Alert,
+ EventSubscription,
SafeAreaView,
StyleSheet,
Text,
TextInput,
Button,
} from 'react-native';
import NativeLocalStorage from './specs/NativeLocalStorage';
const EMPTY = '<empty>';
function App(): React.JSX.Element {
const [value, setValue] = React.useState<string | null>(null);
+ const [key, setKey] = React.useState<string | null>(null);
+ const listenerSubscription = React.useRef<null | EventSubscription>(null);
+ React.useEffect(() => {
+ listenerSubscription.current = NativeLocalStorage?.onKeyAdded((pair) => Alert.alert(`New key added: ${pair.key} with value: ${pair.value}`));
+ return () => {
+ listenerSubscription.current?.remove();
+ listenerSubscription.current = null;
+ }
+ }, [])
const [editingValue, setEditingValue] = React.useState<
string | null
>(null);
- React.useEffect(() => {
- const storedValue = NativeLocalStorage?.getItem('myKey');
- setValue(storedValue ?? '');
- }, []);
function saveValue() {
+ if (key == null) {
+ Alert.alert('Please enter a key');
+ return;
+ }
NativeLocalStorage?.setItem(editingValue ?? EMPTY, key);
setValue(editingValue);
}
function clearAll() {
NativeLocalStorage?.clear();
setValue('');
}
function deleteValue() {
+ if (key == null) {
+ Alert.alert('Please enter a key');
+ return;
+ }
NativeLocalStorage?.removeItem(key);
setValue('');
}
+ function retrieveValue() {
+ if (key == null) {
+ Alert.alert('Please enter a key');
+ return;
+ }
+ const val = NativeLocalStorage?.getItem(key);
+ setValue(val);
+ }
return (
<SafeAreaView style={{flex: 1}}>
<Text style={styles.text}>
Current stored value is: {value ?? 'No Value'}
</Text>
+ <Text>Key:</Text>
+ <TextInput
+ placeholder="Enter the key you want to store"
+ style={styles.textInput}
+ onChangeText={setKey}
+ />
+ <Text>Value:</Text>
<TextInput
placeholder="Enter the text you want to store"
style={styles.textInput}
onChangeText={setEditingValue}
/>
<Button title="Save" onPress={saveValue} />
+ <Button title="Retrieve" onPress={retrieveValue} />
<Button title="Delete" onPress={deleteValue} />
<Button title="Clear" onPress={clearAll} />
</SafeAreaView>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
text: {
margin: 10,
fontSize: 20,
},
textInput: {
margin: 10,
height: 40,
borderColor: 'black',
borderWidth: 1,
paddingLeft: 5,
paddingRight: 5,
borderRadius: 5,
},
});
export default App;
There are a few relevant changes to look at:
- You need to import the
EventSubscriptiontype fromreact-nativeto handle theEventSubscription - You need to use a
useRefto keep track of theEventSubscriptionreference - You register the listener using an
useEffecthook. TheonKeyAddedfunction takes a callback with an object of typeKeyValuePairas a function parameter. - The callback added to
onKeyAddedis executed every time the event is emitted from Native to JS. - In the
useEffectcleanup function, youremovethe event subscription and you set the ref tonull.
The rest of the changes are regular React changes to improve the App for this new feature.
Step 4: Write your Native Code
With everything prepared, let's start writing native platform code.
- Android
- iOS
Assuming you followed the guide for iOS described in the Native Modules guide, what's left to do is to plug the code that emit the events in your app.
To do so, you have to:
- Open the
NativeLocalStorage.ktfile - Modify it as it follows:
package com.nativelocalstorage
import android.content.Context
import android.content.SharedPreferences
import com.nativelocalstorage.NativeLocalStorageSpec
+import com.facebook.react.bridge.Arguments
import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactApplicationContext
+import com.facebook.react.bridge.WritableMap
class NativeLocalStorageModule(reactContext: ReactApplicationContext) : NativeLocalStorageSpec(reactContext) {
override fun getName() = NAME
override fun setItem(value: String, key: String) {
+ var shouldEmit = false
+ if (getItem(key) != null) {
+ shouldEmit = true
+ }
val sharedPref = getReactApplicationContext().getSharedPreferences("my_prefs", Context.MODE_PRIVATE)
val editor = sharedPref.edit()
editor.putString(key, value)
editor.apply()
+ if (shouldEmit == true) {
+ val eventData = Arguments.createMap().apply {
+ putString("key", key)
+ putString("value", value)
+ }
+ emitOnKeyAdded(eventData)
+ }
}
override fun getItem(key: String): String? {
val sharedPref = getReactApplicationContext().getSharedPreferences("my_prefs", Context.MODE_PRIVATE)
val username = sharedPref.getString(key, null)
return username.toString()
}
First, you need to import a couple of types that you need to use to create the eventData that needs to be sent from Native to JS. These imports are:
import com.facebook.react.bridge.Argumentsimport com.facebook.react.bridge.WritableMap
Secondly, you need to implement the logic that actually emits the event to JS. In case of complex types, like the KeyValuePair defined in the specs, Codegen will generate a function that expects a ReadableMap as a parameter. You can create the ReadableMap by using the Arguments.createMap() factory method, and use the apply function to populate the map. It's your responsibility to make sure that the the keys you are using in the map are the same properties that are defined in the spec type in JS.
Assuming you followed the guide for iOS described in the Native Modules guide, what's left to do is to plug the code that emit the events in your app.
To do so, you have to:
- Open the
RCTNativeLocalStorage.hfile. - Change the base class from
NSObjecttoNativeLocalStorageSpecBase
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import <NativeLocalStorageSpec/NativeLocalStorageSpec.h>
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
-@interface RCTNativeLocalStorage : NSObject <NativeLocalStorageSpec>
+@interface RCTNativeLocalStorage : NativeLocalStorageSpecBase <NativeLocalStorageSpec>
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
- Open the
RCTNativeLocalStorage.mmfile. - Modify it to emit the events when needed, for example:
- (void)setItem:(NSString *)value key:(NSString *)key {
+ BOOL shouldEmitEvent = NO;
+ if (![self getItem:key]) {
+ shouldEmitEvent = YES;
+ }
[self.localStorage setObject:value forKey:key];
+ if (shouldEmitEvent) {
+ [self emitOnKeyAdded:@{@"key": key, @"value": value}];
+ }
}
The NativeLocalStorageSpecBase is a base class that provides the emitOnKeyAdded method and its basic implementation and boilerplate. Thanks to this class, you don't have to handle all the conversion between Objective-C and JSI that is required to send the event to JS.
In case of complex types, like the KeyValuePair defined in the specs, Codegen will generate a generic dictionary that you can populate on the native side. It's your responsibility to make sure that the the keys you are using in the dictionary are the same properties that are defined in the spec type in JS.
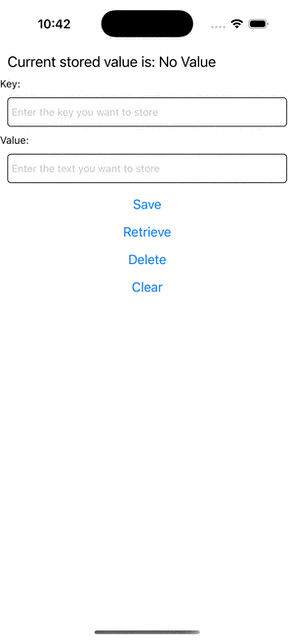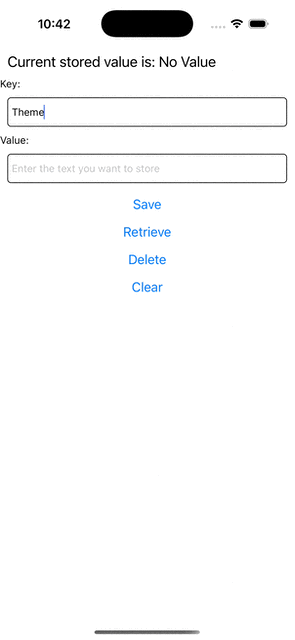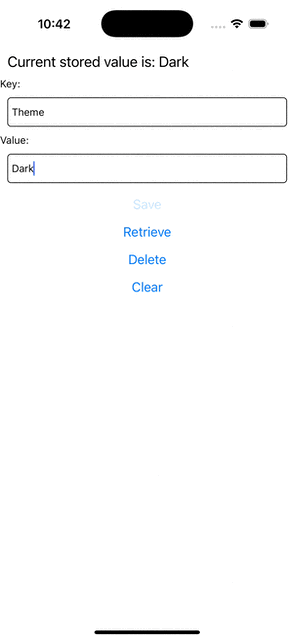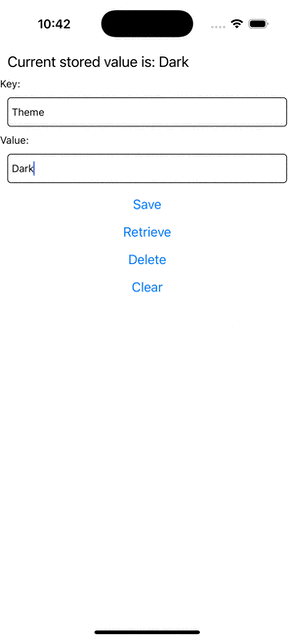
Step 5: Run Your App
If you now try to run your app, you should see this behavior.
 |  |