Invoking native functions on your native component
In the base guide to write a new Native Component, you have explored how to create a new component, how to pass properties from the JS side to the native side, and how to emit events from native side to JS.
Custom components can also call some of the functions implementated in the native code imperatively, to achieve some more advanced functionalities, such as programmatically reload a web page.
In this guide you'll learn how to achieve this, by using a new concept: Native Commands.
This guide starts from the Native Components guide and assumes that you are familiar with it and that you are familiar with Codegen.
1. Update your component specs
The first step is to update the component spec to declare the NativeCommand.
- TypeScript
- Flow
Update the WebViewNativeComponent.ts as it follows:
import type {HostComponent, ViewProps} from 'react-native';
import type {BubblingEventHandler} from 'react-native/Libraries/Types/CodegenTypes';
import codegenNativeComponent from 'react-native/Libraries/Utilities/codegenNativeComponent';
+import codegenNativeCommands from 'react-native/Libraries/Utilities/codegenNativeCommands';
type WebViewScriptLoadedEvent = {
result: 'success' | 'error';
};
export interface NativeProps extends ViewProps {
sourceURL?: string;
onScriptLoaded?: BubblingEventHandler<WebViewScriptLoadedEvent> | null;
}
+interface NativeCommands {
+ reload: (viewRef: React.ElementRef<HostComponent<NativeProps>>) => void;
+}
+export const Commands: NativeCommands = codegenNativeCommands<NativeCommands>({
+ supportedCommands: ['reload'],
+});
export default codegenNativeComponent<NativeProps>(
'CustomWebView',
) as HostComponent<NativeProps>;
Update the WebViewNativeComponent.js as it follows:
// @flow strict-local
import type {HostComponent, ViewProps} from 'react-native';
import type {BubblingEventHandler} from 'react-native/Libraries/Types/CodegenTypes';
import codegenNativeComponent from 'react-native/Libraries/Utilities/codegenNativeComponent';
+import codegenNativeCommands from 'react-native/Libraries/Utilities/codegenNativeCommands';
type WebViewScriptLoadedEvent = $ReadOnly<{|
result: "success" | "error",
|}>;
type NativeProps = $ReadOnly<{|
...ViewProps,
sourceURL?: string;
onScriptLoaded?: BubblingEventHandler<WebViewScriptLoadedEvent>?;
|}>;
+interface NativeCommands {
+ reload: (viewRef: React.ElementRef<HostComponent<NativeProps>>) => void;
+}
+export const Commands: NativeCommands = codegenNativeCommands<NativeCommands>({
+ supportedCommands: ['reload'],
+});
export default (codegenNativeComponent<NativeProps>(
'CustomWebView',
): HostComponent<NativeProps>);
These changes requires you to:
- Import the
codegenNativeCommandsfunction fromreact-native. This instruct codegen that it has to generate the code forNativeCommands - Define an interface that contains the methods we want to invoke in native. All the Native Commands must have a first parameter of type
React.ElementRef. - Export the
Commandsvariable that is the result of the invocation ofcodegenNativeCommands, passing a list of the supported commands.
In TypeScript, the React.ElementRef is deprecated. The correct type to use is actually React.ComponentRef. However, due to a bug in Codegen, using ComponentRef will crash the app. We have the fix already, but we need to release a new version of React Native to apply it.
2. Update the App code to use the new command
Now you can use the command in the the app.
- TypeScript
- Flow
Open the App.tsx file and modify it as it follows:
import React from 'react';
-import {Alert, StyleSheet, View} from 'react-native';
-import WebView from '../specs/WebViewNativeComponent';
+import {Alert, StyleSheet, Pressable, Text, View} from 'react-native';
+import WebView, {Commands} from '../specs/WebViewNativeComponent';
function App(): React.JSX.Element {
+ const webViewRef = React.useRef<React.ElementRef<typeof View> | null>(null);
+
+ const refresh = () => {
+ if (webViewRef.current) {
+ Commands.reload(webViewRef.current);
+ }
+ };
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<WebView
+ ref={webViewRef}
sourceURL="https://react.dev/"
style={styles.webview}
onScriptLoaded={() => {
Alert.alert('Page Loaded');
}}
/>
+ <View style={styles.tabbar}>
+ <Pressable onPress={refresh} style={styles.button}>
+ {({pressed}) => (
+ !pressed ? <Text style={styles.buttonText}>Refresh</Text> : <Text style={styles.buttonTextPressed}>Refresh</Text>) }
+ </Pressable>
+ </View>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: 'center',
alignContent: 'center',
},
webview: {
width: '100%',
- height: '100%',
+ height: '90%',
},
+ tabbar: {
+ flex: 1,
+ backgroundColor: 'gray',
+ width: '100%',
+ alignItems: 'center',
+ alignContent: 'center',
+ },
+ button: {
+ margin: 10,
+ },
+ buttonText: {
+ fontSize: 20,
+ fontWeight: 'bold',
+ color: '#00D6FF',
+ width: '100%',
+ },
+ buttonTextPressed: {
+ fontSize: 20,
+ fontWeight: 'bold',
+ color: '#00D6FF77',
+ width: '100%',
+ },
});
export default App;
Open the App.tsx file and modify it as it follows:
import React from 'react';
-import {Alert, StyleSheet, View} from 'react-native';
-import WebView from '../specs/WebViewNativeComponent';
+import {Alert, StyleSheet, Pressable, Text, View} from 'react-native';
+import WebView, {Commands} from '../specs/WebViewNativeComponent';
function App(): React.JSX.Element {
+ const webViewRef = React.useRef<React.ElementRef<typeof View> | null>(null);
+
+ const refresh = () => {
+ if (webViewRef.current) {
+ Commands.reload(webViewRef.current);
+ }
+ };
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<WebView
+ ref={webViewRef}
sourceURL="https://react.dev/"
style={styles.webview}
onScriptLoaded={() => {
Alert.alert('Page Loaded');
}}
/>
+ <View style={styles.tabbar}>
+ <Pressable onPress={refresh} style={styles.button}>
+ {({pressed}) => (
+ !pressed ? <Text style={styles.buttonText}>Refresh</Text> : <Text style={styles.buttonTextPressed}>Refresh</Text>) }
+ </Pressable>
+ </View>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: 'center',
alignContent: 'center',
},
webview: {
width: '100%',
- height: '100%',
+ height: '90%',
},
+ tabbar: {
+ flex: 1,
+ backgroundColor: 'gray',
+ width: '100%',
+ alignItems: 'center',
+ alignContent: 'center',
+ },
+ button: {
+ margin: 10,
+ },
+ buttonText: {
+ fontSize: 20,
+ fontWeight: 'bold',
+ color: '#00D6FF',
+ width: '100%',
+ },
+ buttonTextPressed: {
+ fontSize: 20,
+ fontWeight: 'bold',
+ color: '#00D6FF77',
+ width: '100%',
+ },
});
export default App;
The relevant changes here are the following:
- Import the
Commandsconst from the spec file. The Command is an object that let us call the methods we have in native. - Declare a ref to the
WebViewcustom native component usinguseRef. You need to pass this ref to the native command. - Implement the
refreshfunction. This function checks that the WebView's ref is not null and if not, it calls the command. - Add a pressable to call the command when the user taps on the button.
The remaining changes are regular React changes to add a Pressable and to style the view so it looks nicer.
3. Rerun Codegen
Now that the specs are updated and the code is ready to use the command, it is time to implement the Native code. However, before diving into writing native code, you have to rerun codegen, to let it generate the new types that are needed by the Native code.
- Android
- iOS
Codegen is executed through the generateCodegenArtifactsFromSchema Gradle task:
cd android
./gradlew generateCodegenArtifactsFromSchema
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 837ms
14 actionable tasks: 3 executed, 11 up-to-date
This is automatically run when you build your Android application.
Codegen is run as part of the script phases that's automatically added to the project generated by CocoaPods.
cd ios
bundle install
bundle exec pod install
The output will look like this:
...
Framework build type is static library
[Codegen] Adding script_phases to ReactCodegen.
[Codegen] Generating ./build/generated/ios/ReactCodegen.podspec.json
[Codegen] Analyzing /Users/me/src/TurboModuleExample/package.json
[Codegen] Searching for codegen-enabled libraries in the app.
[Codegen] Found TurboModuleExample
[Codegen] Searching for codegen-enabled libraries in the project dependencies.
[Codegen] Found react-native
...
4. Implement the Native Code
Now it's time to implement the native changes that will enable your JS to directly invoke methods on your native view.
- Android
- iOS
To let your view respond to the Native Command, you only have to modify the ReactWebViewManager.
If you try to build right now, the build will fail, because the current ReactWebViewManager does not implement the new reload method.
To fix the build error, let's modify the ReactWebViewManager to implement it.
- Java
- Kotlin
//...
@ReactProp(name = "sourceUrl")
@Override
public void setSourceURL(ReactWebView view, String sourceURL) {
if (sourceURL == null) {
view.emitOnScriptLoaded(ReactWebView.OnScriptLoadedEventResult.error);
return;
}
view.loadUrl(sourceURL, new HashMap<>());
}
+ @Override
+ public void reload(ReactWebView view) {
+ view.reload();
+ }
public static final String REACT_CLASS = "CustomWebView";
//...
@ReactProp(name = "sourceUrl")
override fun setSourceURL(view: ReactWebView, sourceURL: String?) {
if (sourceURL == null) {
view.emitOnScriptLoaded(ReactWebView.OnScriptLoadedEventResult.error)
return;
}
view.loadUrl(sourceURL, emptyMap())
}
+ override fun reload(view: ReactWebView) {
+ view.reload()
+ }
companion object {
const val REACT_CLASS = "CustomWebView"
}
In this case, it's enough to call directly the view.reload() method because our ReactWebView inherits from the Android's WebView and it has a reload method directly available. If you are implementing a custom function, that is not available in your custom view, you might also have to implement the required method in the Android's View that is managed by the React Native's ViewManager.
To let your view respond to the Native Command, we need to implement a couple of methods on iOS.
Let's open the RCTWebView.mm file and let's modify it as it follows:
// Event emitter convenience method
- (const CustomWebViewEventEmitter &)eventEmitter
{
return static_cast<const CustomWebViewEventEmitter &>(*_eventEmitter);
}
+ - (void)handleCommand:(const NSString *)commandName args:(const NSArray *)args
+ {
+ RCTCustomWebViewHandleCommand(self, commandName, args);
+ }
+
+ - (void)reload
+ {
+ [_webView reloadFromOrigin];
+ }
+ (ComponentDescriptorProvider)componentDescriptorProvider
{
return concreteComponentDescriptorProvider<CustomWebViewComponentDescriptor>();
}
To make your view respond to the Native Commands, you need to apply the following changes:
- Add a
handleCommand:argsfunction. This function is invoked by the components infrastructure to handle the commands. The function implementation is similar for every component: you need to call anRCT<componentNameInJS>HandleCommandfunction that is generated by Codegen for you. TheRCT<componentNameInJS>HandleCommandperform a bunch of validation, verifying that the command that we need to invoke is among the supported ones and that the parameters passed matches the one expected. If all the checks pass, theRCT<componentNameInJS>HandleCommandwill then invoke the proper native method. - Implement the
reloadmethod. In this example, thereloadmethod calls thereloadFromOriginfunction of the WebKit's WebView.
5. Run your app
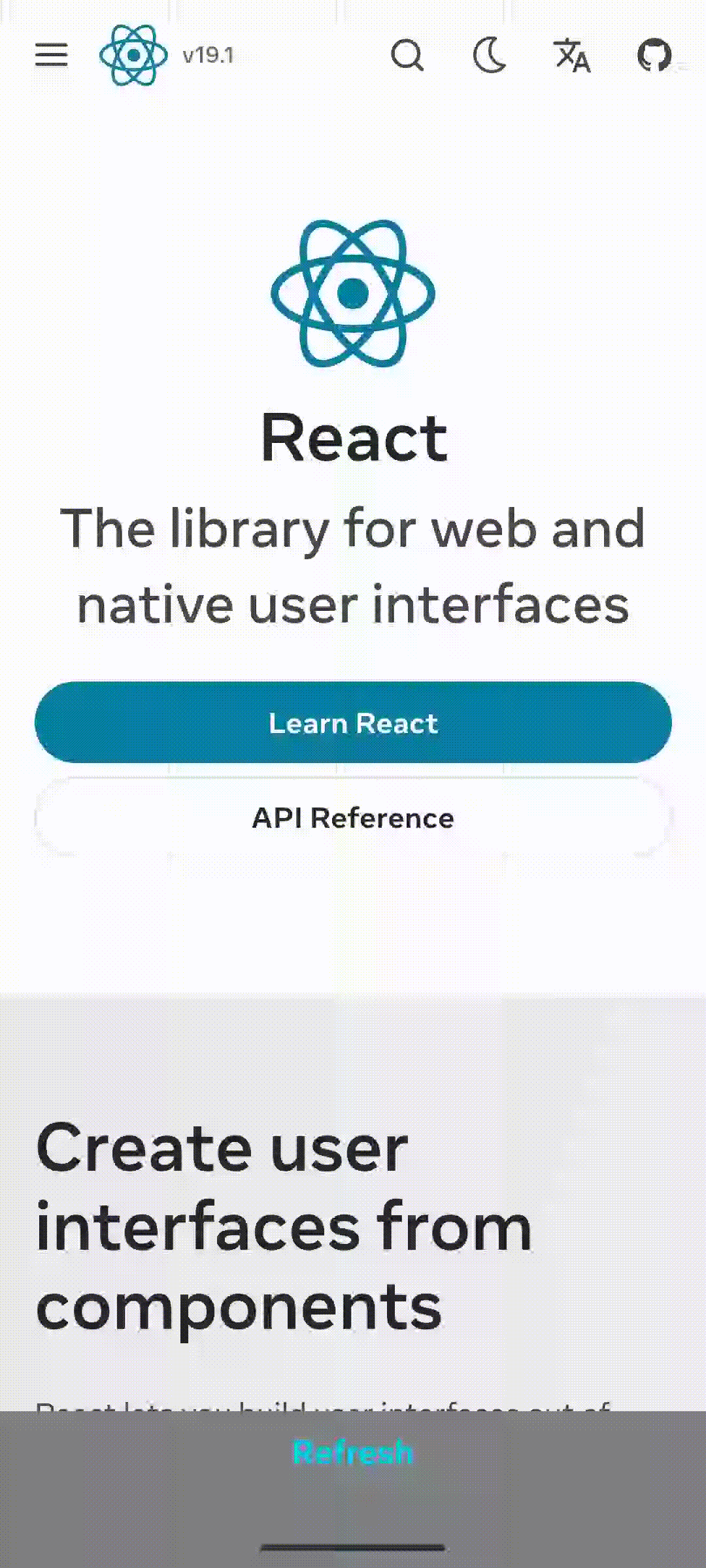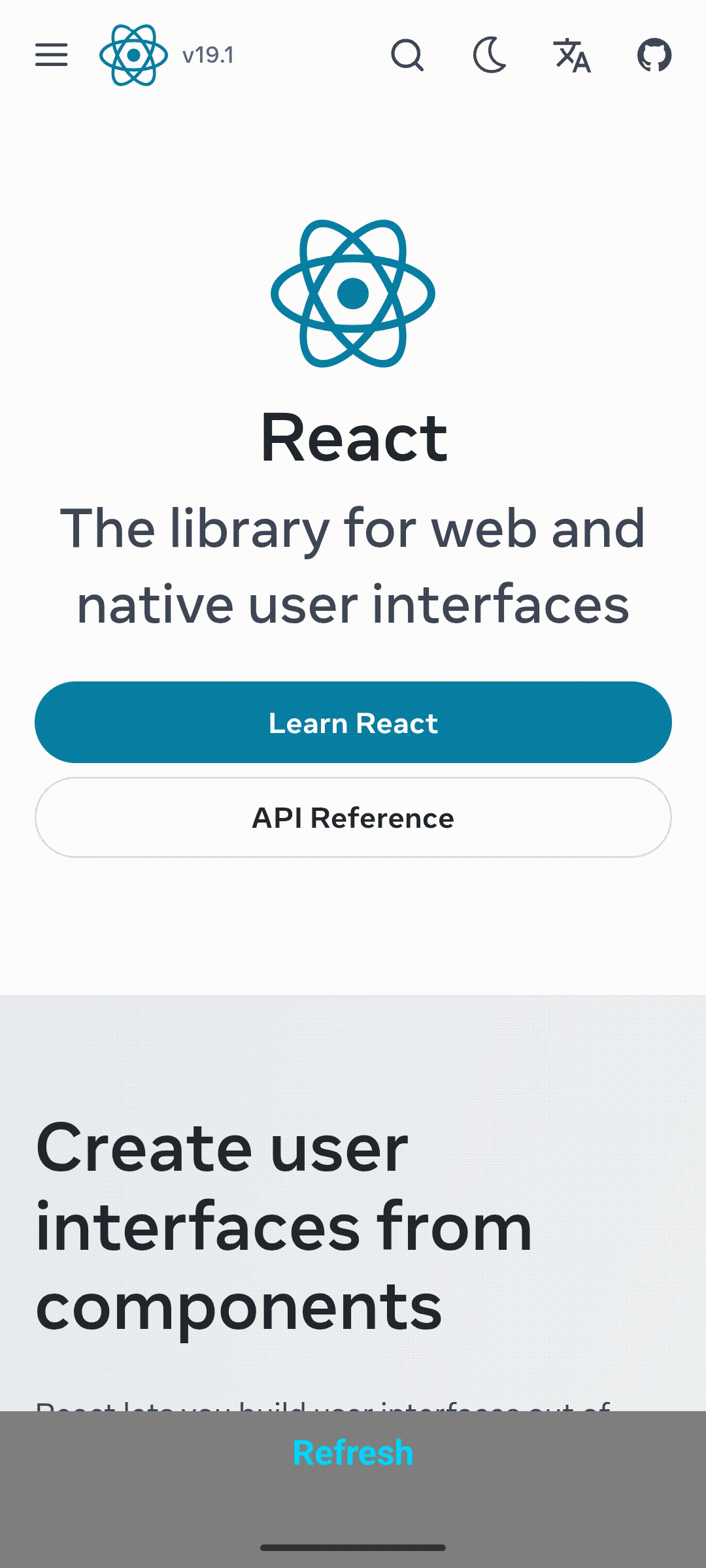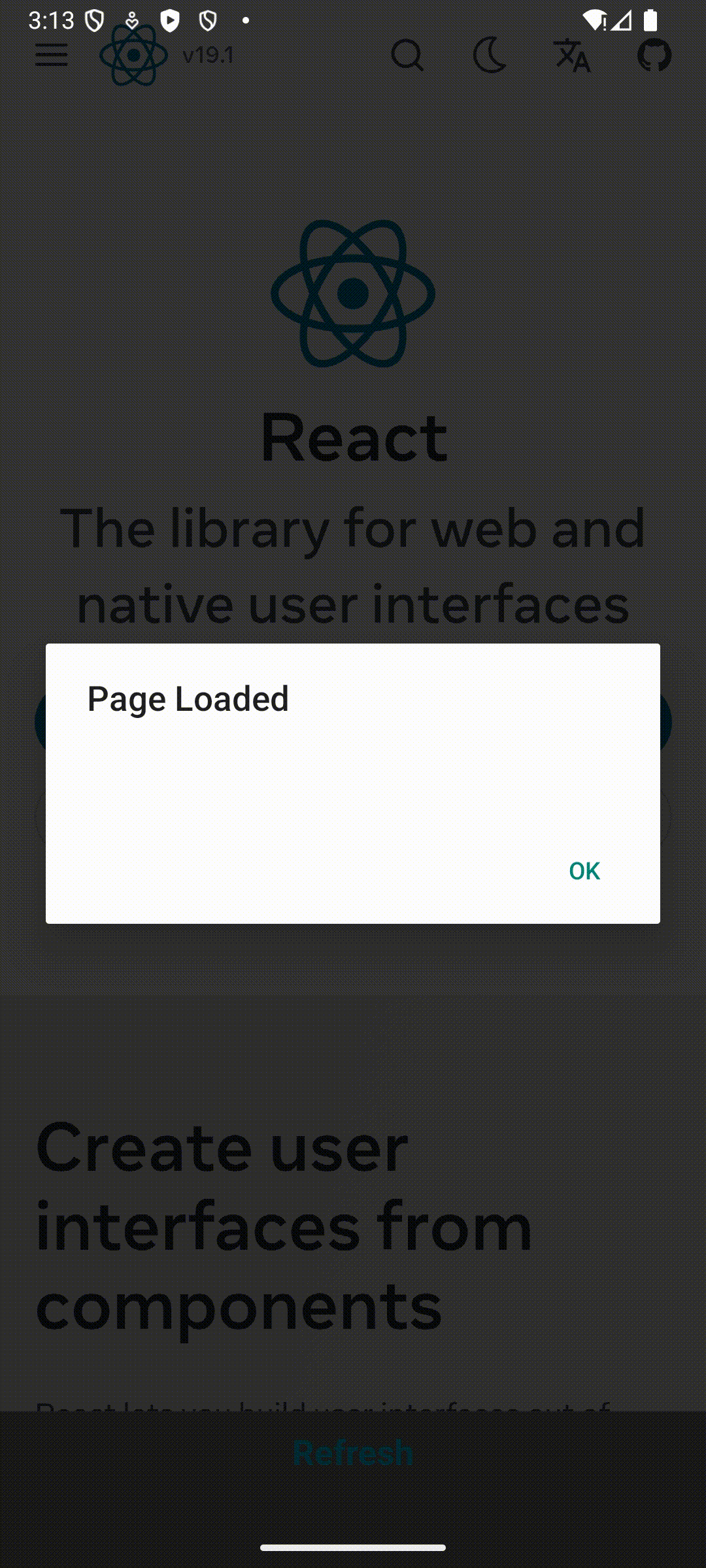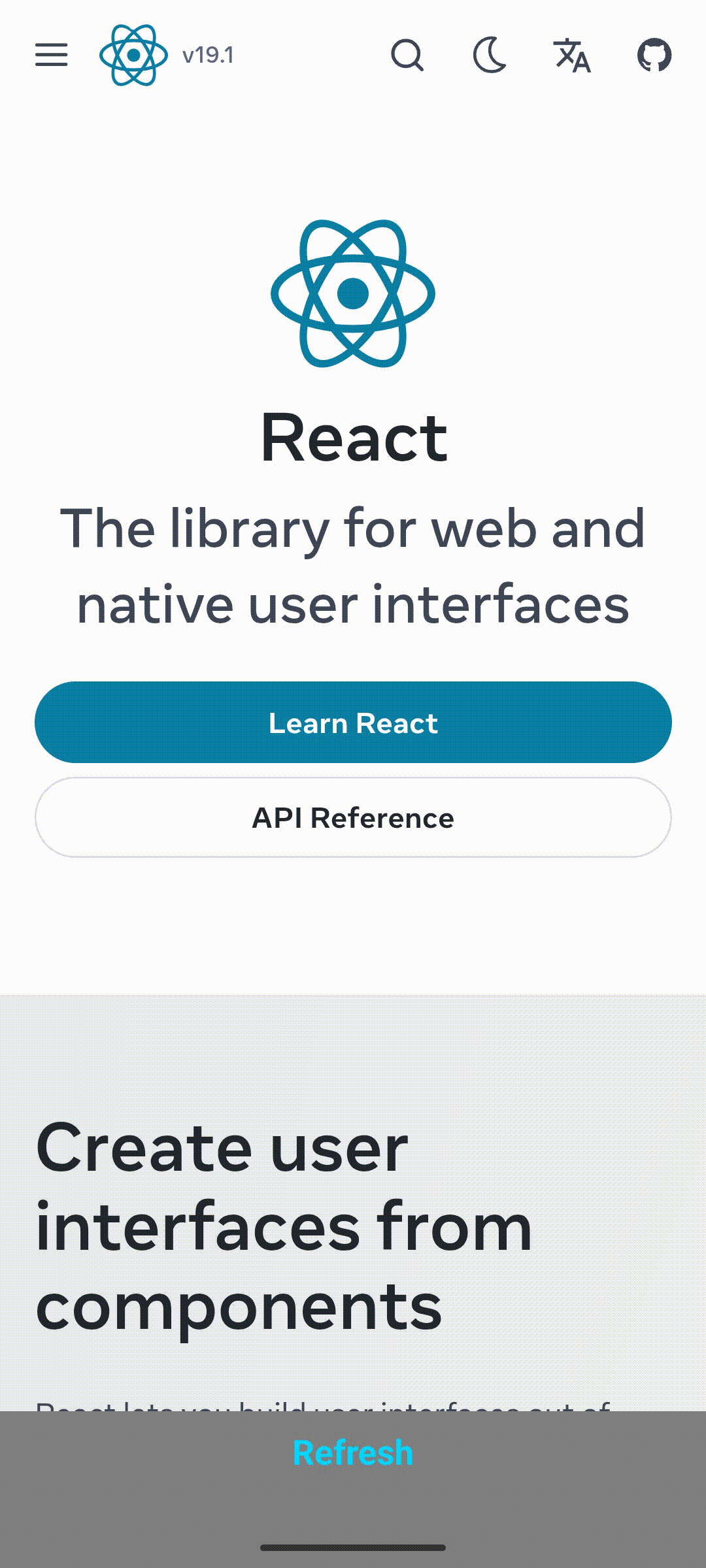
Finally, you can run your app with the usual commands. Once the app is running, you can tap on the refresh button to see the page getting reloaded.
 |  |